Administering the WebLogic Server with Admin commands
LICENSES
PING
SHUTDOWN
VERSION
LIST
CONNECT
RESET_POOL
LOCK
UNLOCK
Setting up multihoming
This document describes how to use the WebLogic Server Admin commands and how to set up Multihoming on your machine.
Before you can run the WebLogic Server the first time, you will need to
install and configure it. Read Installing
WebLogic Server.

Administering the WebLogic Server with Admin commands
The WebLogic Server is administered by calls to the weblogic.Admin class. You can also
make programmatic calls to administrative information from a
WebLogic client. Check the document, Writing a WebLogic client application, for more information.
All Admin commands follow a similar pattern. You can get a list
of commands by entering the following:
java weblogic.Admin
General syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL command arguments
Arguments
- URL
- The URL
 of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP
of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests. The scheme
of the URL is "t3://hostname:port".
port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests. The scheme
of the URL is "t3://hostname:port".
- command
-
- arguments
- Each command may have a set of optional and/or required arguments.
For example, the SHUTDOWN command requires a password to the WebLogic Server.


connect
This command makes the specified number of connections to the WebLogic Server
and returns the number of total time for each round trip and the
average milliseconds per connection.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL CONNECT count user password
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- count
- Number of connections to make.
- user (optional)
- Default = guest
- password (optional)
- Default = guest
Example
This makes 100 connections to the WebLogic Server on port 7001 of the
host xyz.com.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:7001 CONNECT 100 guest guest


licenses
Lists the licenses of the WebLogic Server instances installed
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL LICENSES round_trips message_length user password
Arguments
- user (optional)
- Default = guest
- password (optional)
- Default = guest
Example
This command requests the license information for a WebLogic Server running on port 6789 of machine xyz.com.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:6789 LICENSES guest guest


list
Lists the bindings of a node in the JNDI naming tree.
naming tree.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin context LIST user password
Arguments
- context
- The JNDI context (for example weblogic, weblogic.ejb, javax) for lookup.
- username
- Username of a T3User that has permissions to
exercise a JNDI lookup for this node.
- password
- Password of a T3User that has permissions to
exercise a JNDI lookup for this node.


lock
Locks WebLogic against non-privileged logins. Subsequent login attempts
will initiate a SecurityException that contains an optional string message.
This command requires an administrative username and password.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL LOCK system passwd string_message
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- password
- Administrator password to the WebLogic Server. The WebLogic Server
password is set in the weblogic.properties file. The username for the
administrator is always "system", and both username and password must
be supplied for this command.
- string_message
- Message (in double quotes) to be supplied in the SecurityException
thrown if a non-privileged user attempts to login while the WebLogic
Server is locked.
Example
This command locks WebLogic; any application attempting to login with a
non-privileged T3User username and password will receive the message,
"Sorry, WebLogic is temporarily out of service."
java weblogic.Admin t3://bigbox.com:7001 LOCK system gumby1234
"Sorry, WebLogic is temporarily out of service."


ping
Verifies that a WebLogic Server is listening on a port and is ready to accept
WebLogic client requests.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL PING round_trips message_length user password
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- round_trips (optional)
- Number of pings.
- message_length (optional)
- Packet to send in each ping. Ping requests over 10Mb in size will
throw an exception.
- user (optional)
- Default = guest
- password (optional)
- Default = guest
Example
This command pings a WebLogic Server running on port 6789 of machine xyz.com.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:6789 PING 10


reset_pool
This command resets the connections in a registered connection
pool. For more information on setting up and using connection pools,
see the Developers Guide
for WebLogic JDBC.
This is a privileged command. You must supply the password for the
WebLogic Server administrative user to use this command. You must know the
name of the connection pool, which is an entry in the WebLogic Server's weblogic.properties file.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL RESET_POOL poolName system password
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number
of the TCP port at which WebLogic is listening for client requests;
use "t3://host:port."
- poolName
- Name of a connection
pool as it is registered in the WebLogic Server's
weblogic.properties file.
- password
- Administrative password for the user "system". You must supply the
username "system" and the administrative password to use this
Admin command.
Example
This command refreshes the connection pool registered as "eng" for the
WebLogic Server listening on port 7001 of the host xyz.com.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:7001 RESET_POOL eng system gumby


shutdown
Shuts down a WebLogic Server.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL SHUTDOWN system password
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- password
- Administrator password to the WebLogic Server. The WebLogic Server
password is set in the weblogic.properties file. The username for the
administrator is always "system", and both username and password must
be supplied for this command.
Example
This command shuts down a WebLogic Server listening on port 7001 of machine
xyz.com with an administrative password of gumby.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:7001 SHUTDOWN system gumby


unlock
Unlocks WebLogic after a lock operation.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL UNLOCK system passwd
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- password
- Administrator password to the WebLogic Server. The WebLogic Server
password is set in the weblogic.properties file. The username for the
administrator is always "system", and both username and password must
be supplied for this command.
Example
This command unlocks WebLogic, following a lock
operation.
java weblogic.Admin t3://bigbox.com:7001 UNLOCK system gumby1234


version
Displays the version of the WebLogic Server.
Syntax
java weblogic.Admin URL VERSION user password
Arguments
- URL
- The URL of the WebLogic Server host and port number of the TCP port
at which WebLogic is listening for client requests; use
"t3://host:port."
- user (optional)
- Default = guest
- password (optional)
- Default = guest
Example
This command displays the version for a WebLogic Server running on port 7001
of xyz.com.
java weblogic.Admin t3://xyz.com:7001 VERSION guest guest


Setting up multihoming
Multihoming means setting up more than one IP address on a single machine. You can run multiple WebLogic Servers on
a multihomed machine. Each is reachable at a different IP address and
a port that may be the same for all WebLogic Servers (as when you have
multiple WebLogic Servers listening for HTTP requests on multiple IP
addresses, but all on port 80). Multihoming is one way to try out
WebLogic clustering
address on a single machine. You can run multiple WebLogic Servers on
a multihomed machine. Each is reachable at a different IP address and
a port that may be the same for all WebLogic Servers (as when you have
multiple WebLogic Servers listening for HTTP requests on multiple IP
addresses, but all on port 80). Multihoming is one way to try out
WebLogic clustering if you only have one machine available for
testing. For more information see Administering
a WebLogic Server Cluster.
if you only have one machine available for
testing. For more information see Administering
a WebLogic Server Cluster.
A WebLogic Server's address is a combination of its IP address and the
port at which it is listening for login requests. When you set up a
machine to run a single WebLogic Server, you must set the listen port
with the property weblogic.system.listenPort. If you do not set a bind
address, the WebLogic Server will accept any request that comes into
that port, regardless of the IP address. That is, if the bind address
is not set, the WebLogic Server will bind to the IP address designation
"any," which translates to any of the IP addresses set for the
machine.
Several properties may be involved in setting up a multihomed machine
to support multiple WebLogic Servers. You will set these properties in
each per-server properties file,
or -- if you have a global properties file and have established a per-server directory for each
server -- you may use -D options to set these properties on the
command line.
- weblogic.system.bindAddr
- Set the bind address to the IP address or domain name at which
the WebLogic Server will be reachable.
- weblogic.system.listenPort
- Set the port at which each WebLogic Server should listen for login
requests. You may set the same port with multiple servers using
different IP addresses; for example, if you have multiple servers
listening for HTTP requests, they might each be listening on a
different IP address, but all on port 80.
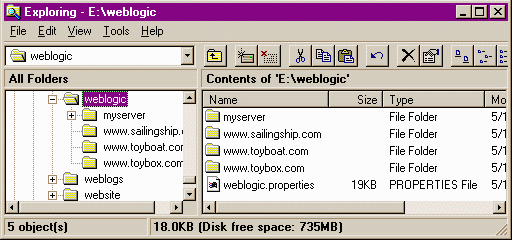
- weblogic.system.name
- Set the name of each WebLogic Server. The system name will appear in
the Console and the Admin servlet pages. A directory that matches
each system name must be present in the weblogic.system.home directory, which by default is
\weblogic. For example, here is the directory structure to support 3
WebLogic Servers all listening on port 80 on different IP addresses:
- They all use the same global properties file, which sets the
listen port to 80 and is present in the weblogic.system.home directory. Each is started by
setting the following properties on the command line (you will need to
substitute the correct bindAddr for each server):
$ java ... -Dweblogic.system.name=www.toyboat.com
-Dweblogic.system.bindAddr=192.0.0.1 ...
- weblogic.system.acceptBacklog
- The number of connection requests the server will accept before
refusing additional requests. The default value is 50 and the maximum
value is OS dependant.
Each per-server directory will have its own weblogic.log, located in
the directory corresponding to the server name. Place security
certificates for each WebLogic Server in the appropriate per-server
directory.
We include a few brief instructions here on how to add IP addresses,
but in general you should ask your system or network administrator
about assigning multiple IP addresses. There may be issues that affect
your network environment.
How to add IP addresses on your Windows NT machine
Note that in some configurations, including machines with Virtual
Private Network (VPN) clients, Multihoming may not function correctly.
- In the Start menu, choose Settings, and then open
the Control Panel.
- Double-click the Network icon.
- Select the Protocols tab.
- Highlight "TCP/IP Protocol."
- Click the Protocols button.
- Click the Advanced button.
- In the IP Addresses panel, click the Add button.
- Set the new IP address and subnet mask and click the
Add button.
- Click the OK button on each panel.
These instructions are specific for Solaris. Most UNIX systems should
work the same way. Generally speaking, you use the
ifconfig command to set up multiple IP addresses,
but the exact syntax depends on the platform and OS version.
Note that if you want these settings to remain after a re-boot, you
will need to modify the appropriate startup scripts.



