All Examples XML Examples
package examples.xml.jms
XML-JMS example package and classes
about this example
This example illustrates:
- Generating XML data using the DOM API
- Parsing XML data using a validating DOM parser
- Passing XML data between two client applications via JMS TextMessages
- Implementing a custom EntityResolver
- Using JMS selectors to filter JMS messages from a queue
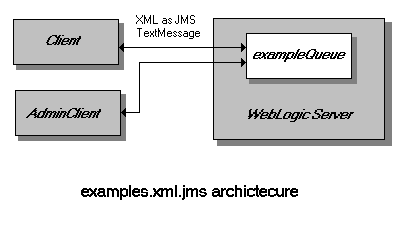
This example represents a simple workflow system.
Client accepts user
input to define a message that must be approved by
AdminClient.
The message is combined in the form of an XML document with the name
of the user who sent the message and the current status of the
message. The XML data is sent as a JMS text
message to a queue where it awaits approval from
AdminClient.
The AdminClient
updates attributes of the XML data and returns
it to the queue. The message is then read back in by
Client which
parses the XML data using a validating DOM parser and displays the results
in the console. The parser uses
ResourceEntityResolver to resolve
the external DTDs when validating the documents. All messages are sent to the same JMS queue and are
filtered by Client
and AdminClient using JMS
selectors.
how to use this example
Build the example:
- Set up your development shell, as described in
Setting up
your environment.
-
Compile the files in this directory as shown in this example for Windows NT:
$ javac -d %CLIENT_CLASSES% *.java
Configure the server:
- Configure a JMS connection pool by un-commenting the following lines
in your weblogic.properties file.
weblogic.jdbc.connectionPool.demoPool=\
url=jdbc:cloudscape:demo,\
driver=COM.cloudscape.core.JDBCDriver,\
initialCapacity=1,\
maxCapacity=5,\
capacityIncrement=2
props=user=none;password=none;server=none
weblogic.allow.reserve.weblogic.jdbc.connectionPool.demoPool=everyone
weblogic.jms.connectionPool=demoPool
java.system.property.cloudscape.system.home=WebLogicHome/eval/cloudscape/data
where WebLogicHome is the
installation directory of WebLogic Server.
- In this example, the parser validates the XML documents against the
workflow.dtd DTD. The DTD
is an external entity that is resolved by
ResourceEntityResolver.
ResourceEntityResolver expects
to find the DTD in the same directory as the client classes. Before running this
example, you must copy the DTD to the
/myserver/clientclasses/examples/xml/jms directory
under the WebLogic installation directory.
Run the example:
-
Start the WebLogic Server in a new command shell.
-
In your development shell, run the Client
with the following command:
$ java examples.xml.jms.Client t3://hostname:port userName
where:
- hostname
- Host name of the WebLogic Server
- port
- Port where the WebLogic Server is listening for connections
(weblogic.system.ListenPort).
- userName
- Name for the client. This can be anything.
- Enter a message to be approved by
AdminClient.
- To run the AdminClient,
set up a new development shell, as described in
Setting up
your environment, and run the AdminClient
with the following command:
$ java examples.xml.jms.AdminClient t3://hostname:port
where:
- hostname
- Host name of the WebLogic Server
- port
- Port where the WebLogic Server is listening for connections
(weblogic.system.ListenPort).
there's more...
Read more about XML in
Using
XML with WebLogic Server.
Read more about JMS in the Developer Guide,
Using
WebLogic JMS.
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Last updated
2/9/2000

